CANCEL
The core structure of melt pumps primarily consists of the pump housing, gear shaft, sliding bearings, front and rear end covers, and shaft seals. These components work together to ensure the pump's normal operation and high-efficiency performance.
Pump Housing: Serves as the main body of the melt pump, housing the gear shaft and other internal components while providing structural support and stability.
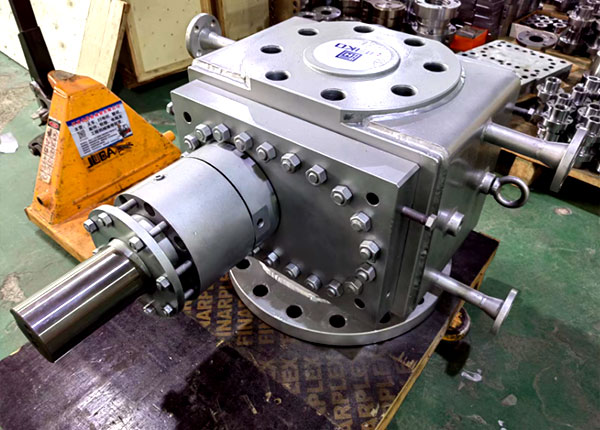

Gear Shaft: Typically composed of high-precision gears that mesh together to convey the melt. The design and material selection of these gears are critical to the pump's efficiency and durability.
Sliding Bearings: Support the rotation of the gear shaft, minimize friction and wear, and ensure stable pump operation.
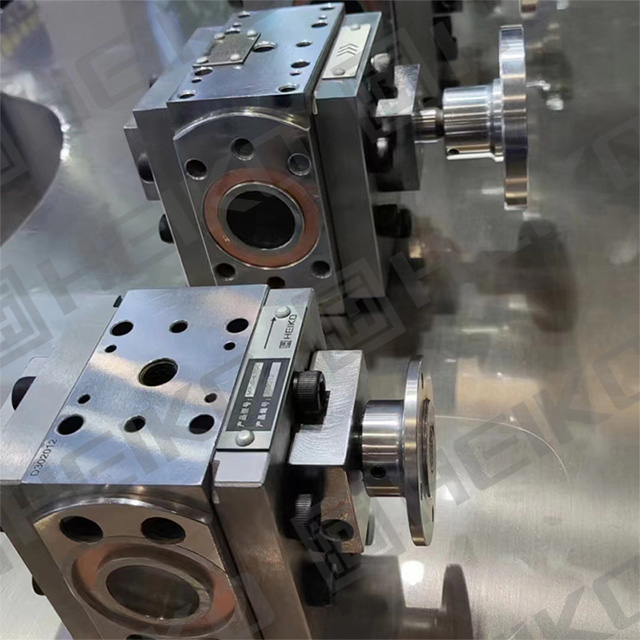
Front and Rear End Covers: Seal both ends of the pump housing to prevent melt leakage and secure the gear shaft and other internal components.
Shaft Seal: Prevents melt leakage from the pump shaft, typically employing mechanical seals or packing seals.
These components collectively form the core structure of the melt pump, enabling efficient and stable melt transportation.
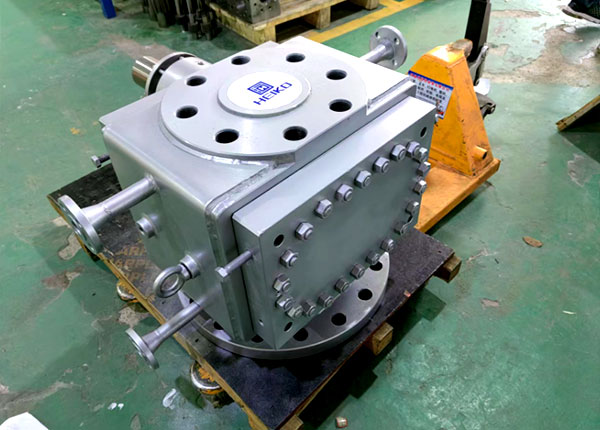

The core structure of melt pumps (primarily the widely adopted external gear type, accounting for over 90% of applications and suited for BOPP/BOPET film extrusion, PA/PP plastic pelletizing, and pipe/sheet extrusion) is engineered for “precision melt conveyance under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions.”
Material selection of melt pump
What materials can the melt pump transport?
Application areas of plastic extrusion melt pumps
Heiko Company had participated in the CHINAPLAS 2024.
Core Structure of Melt Pumps
What is the maximum working pressure of a twin-shaft melt gear pump?
What is a screen changer?
How is the working pressure of a reactor melt-pump adjusted?
Analysis of Core Application Areas for Screen Changers
plastic filament extrusion machine screen changer